SUMMARY: The FDA on May 28, 2021, granted accelerated approval to TRUSELTIQ® (Infigratinib), a kinase inhibitor for adults with previously treated, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic Cholangiocarcinoma with a Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2 (FGFR2) fusion or other rearrangement, as detected by an FDA-approved test. The FDA also approved FoundationOne® CDx (Foundation Medicine, Inc.) for selection of patients with FGFR2 fusion or other rearrangement as a companion diagnostic device for treatment with TRUSELTIQ®.
Bile Duct cancer (Cholangiocarcinoma), comprise about 30% of all primary liver tumors and includes both intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile duct cancers. Klatskin tumor is a type of Cholangiocarcinoma that begins in the hilum, at the junction of the left and right bile ducts. It is the most common type of Cholangiocarcinoma, accounting for more than half of all cases. About 8,000 people in the US are diagnosed with Cholangiocarcinoma each year and approximately 20% of the cases are suitable for surgical resection, whereas a majority of patients at diagnosis have advanced disease. The 5-year survival is less than 5%, with limited progress made over the past two decades.
Approximately 75% of patients are diagnosed with late-stage disease, and are often treated with Gemcitabine plus Cisplatin, based on the findings of the ABC-02 study. Second line treatment options include FOLFOX regimen, which is associated with a Response Rate of about 5%, median Progression Free Survival (PFS) of about 4 months, and median Overall Survival (OS) of about 6 months. There is therefore an unmet need for new effective therapies. FGFRs (Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors) play an important role in tumor cell proliferation and survival, migration and angiogenesis. Activating fusions, rearrangements, translocations and gene amplifications in FGFRs result in dysregulation of FGFR signaling, and may contribute to the pathogenesis of various cancers, including Cholangiocarcinoma. FGFR2 fusions or rearrangements occur almost exclusively in intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma, where they are observed in 10-16% of patients.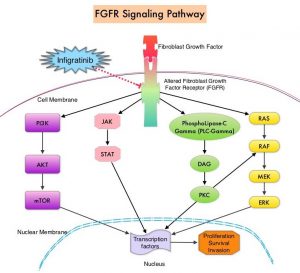
TRUSELTIQ® (Infigratinib) is an orally administered, ATP-competitive, Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor of FGFR, which targets the Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGFR) protein, blocking downstream activity. In clinical studies, TRUSELTIQ® demonstrated a clinically meaningful Overall Response Rate (ORR) and Duration of Response (DOR).
The present FDA approval was based on a multicenter, open-label, single-arm, Phase II trial that enrolled 108 patients with previously treated, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic Cholangiocarcinoma, with an FGFR2 fusion or rearrangement as determined by local or central testing. Patients received TRUSELTIQ® 125 mg orally daily for 21 days of each 28-day cycle, until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. All patients had received at least 1 prior line of systemic therapy and 54% had received 2 or more prior lines of treatment. The median age was 53 years and all patients received prophylaxis with the oral phosphate binder Sevelamer carbonate. The co-Primary endpoints were Objective Response Rate (ORR) by Independent Central Review, and Duration of Response (DOR). Secondary endpoints included Progression Free Survival (PFS), Disease Control Rate (DCR), Overall Survival (OS), Safety and Pharmacokinetics. The median follow up was 10.6 months.
The ORR was 23%, with a median Duration of Response of 5.0 months. Among responding patients, 32% had a Duration of Response of 6 months or more. The median PFS was 7.3 months. The most common toxicities were hyperphosphatemia, increased creatinine, nail toxicity, stomatitis, dry eye, fatigue, alopecia, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, arthralgia, dysgeusia, constipation, abdominal pain, dry mouth, eyelash changes, diarrhea, dry skin, decreased appetite, vision blurred and vomiting. Serious toxicities included hyperphosphatemia and retinal pigment epithelial detachment and monitoring for these adverse reactions during treatment is recommended.
It was concluded that TRUSELTIQ® administered as second or later line treatment was associated with promising anticancer activity, and represents a new therapeutic option for patients with Cholangiocarcinoma and FGFR fusions/rearrangements. A Phase III study of TRUSELTIQ® versus Gemcitabine/Cisplatin is ongoing, in the first-line setting.
Final results from a phase II study of infigratinib (BGJ398), an FGFR-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with previously treated advanced cholangiocarcinoma harboring an FGFR2 gene fusion or rearrangement. Javle MM, Roychowdhury S, Kelley RK, et al. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2021.39.3_suppl.265 Journal of Clinical Oncology 39, no. 3_suppl (January 20, 2021) 265-265.

