SUMMARY: Lung cancer is the second most common cancer in both men and women and accounts for about 13% of all new cancers and 27% of all cancer deaths. It is the leading cause of cancer death among both men and women. The American Cancer Society estimates that over 221,200 new cases of lung cancer will be diagnosed in the United States in 2015 and over 158,000 patients will die of the disease. Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) accounts for approximately 85% of all lung cancers. Of the three main subtypes of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), 30% are Squamous Cell Carcinomas (SCC), 40% are Adenocarcinomas and 10% are Large cell carcinomas.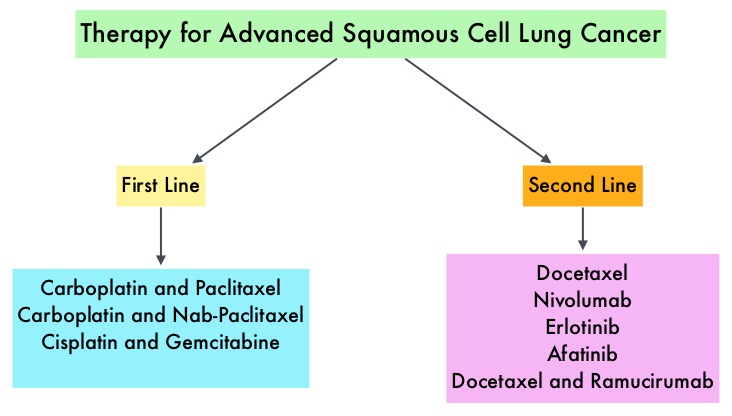 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer patients with squamous cell histology have been a traditionally hard- to-treat patient group, with less than 5% of patients with advanced SCC, surviving for five years or longer. Some of the advanced NSCLC tumors are dependent on the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) for cell proliferation and survival, regardless of EGFR mutation status. TARCEVA® (Erlotinib) is a reversible EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor and is presently approved by the FDA for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC, after failure of at least one prior chemotherapy regimen. GILOTRIF® (Afatinib) is an oral, irreversible blocker of the ErbB family which includes EGFR (ErbB1), HER2 (ErbB2), ErbB3 and ErbB4. This kinase inhibitor is indicated for the first line treatment of patients with metastatic NSCLC, whose tumors have Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) substitution mutations.
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer patients with squamous cell histology have been a traditionally hard- to-treat patient group, with less than 5% of patients with advanced SCC, surviving for five years or longer. Some of the advanced NSCLC tumors are dependent on the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) for cell proliferation and survival, regardless of EGFR mutation status. TARCEVA® (Erlotinib) is a reversible EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor and is presently approved by the FDA for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC, after failure of at least one prior chemotherapy regimen. GILOTRIF® (Afatinib) is an oral, irreversible blocker of the ErbB family which includes EGFR (ErbB1), HER2 (ErbB2), ErbB3 and ErbB4. This kinase inhibitor is indicated for the first line treatment of patients with metastatic NSCLC, whose tumors have Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) substitution mutations.
The LUX-Lung 8 is a phase III trial in which 795 patients with Stage IIIB/IV Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the lung who had progressed on first line platinum based doublet therapy, were randomized 1:1 to receive GILOTRIF 40 mg PO daily (N=398) or TARCEVA 150 mg PO daily (N=397). Treatment was given until disease progression. The median age was 65 years. Majority of the patients were male, caucasian and ex-smokers. The Primary endpoint was Progression Free Survival (PFS) and Secondary endpoints included Overall Survival (OS), Objective Response Rate (ORR), Disease Control Rate (DCR), patient reported outcomes and safety. The Primary endpoint of Progression Free Survival (PFS) was met and reported in 2014 and favored GILOTRIF® over TARCEVA®. The authors in this analysis reported the Overall Survival data, as well as updated data on Progression Free Survival and other Secondary endpoints. The median Overall Survival was 7.9 months with GILOTRIF® and 6.8 months with TARCEVA® (HR=0.81; P=0.008). This meant a 19% reduction in the risk of death with GILOTRIF® when compared to TARCEVA® and this survival advantage was consistent across all time points. The updated median Progression Free Survival for GILOTRIF® was 2.6 months vs 1.9 months for TARCEVA® (HR=0.81; P=0.01). The Disease Control Rate was 50.5% for GILOTRIF® and 39.5% with TARCEVA® (P=0.002). Based on patient reported outcomes, symptoms including cough and dyspnea were better with GILOTRIF® compared to TARCEVA®. Incidence of severe adverse events was similar with both therapies, with patients on GILOTRIF® experiencing more grade 3 diarrhea and stomatitis and patients receiving TARCEVA® experiencing more grade 3 rash. The authors concluded that GILOTRIF® should be the TKI of choice in the second line treatment of patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the lung, as it significantly improves Overall Survival, Progression Free Survival, Disease Control Rate and symptom control, with manageable toxicities, when compared to TARCEVA®. Afatinib (A) vs erlotinib (E) as second-line therapy of patients (pts) with advanced squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the lung following platinum-based chemotherapy: Overall survival (OS) analysis from the global phase III trial LUX-Lung 8 (LL8). Soria J, Felip E, Cobo M, et al. J Clin Oncol 33, 2015 (suppl; abstr 8002)

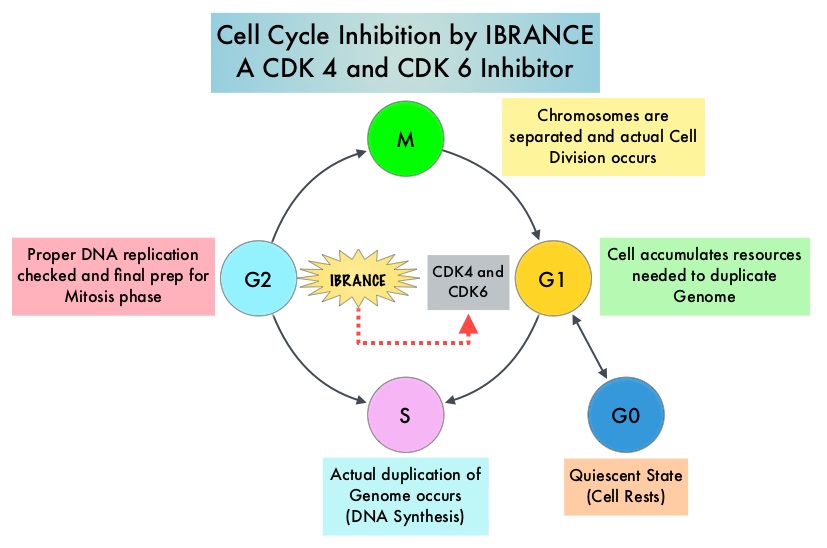 Approximately 80% of breast tumors express Estrogen Receptors and/or Progesterone Receptors and these patients are often treated with anti-estrogen therapy as first line treatment. Cyclin Dependent Kinases (CDK) play a very important role to facilitate orderly and controlled progression of the cell cycle. Genetic alterations in these kinases and their regulatory proteins have been implicated in various malignancies. Cyclin Dependent Kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4 and CDK6) phosphorylate RetinoBlastoma protein (RB) and initiate transition from the G1 phase to the S phase of the cell cycle. CDK4 and CDK6 are activated in hormone receptor positive breast cancer, promoting breast cancer cell proliferation. Further, there is evidence to suggest that endocrine resistant breast cancer cell lines depend on CDK4 for cell proliferation. IBRANCE® (Palbociclib) is a reversible, oral, selective, small molecule inhibitor of Cyclin Dependent Kinases, CDK4 and CDK6, and prevent RB1 phosphorylation. IBRANCE® is the first CDK inhibitor approved by the FDA. It exhibits synergy when combined with endocrine therapies. In an open-label, randomized, phase II study, which included treatment naïve postmenopausal women with ER-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer, IBRANCE® given along with Aromatase Inhibitor FEMARA® (Letrozole) significantly prolonged Progression Free Survival, Overall Response rate and median duration of response, compared to FEMARA® alone. Based on this data, the U. S. Food and Drug Administration on February 3, 2015 granted accelerated approval to IBRANCE® (Palbociclib), for use in combination with FEMARA® (Letrozole) in this patient population. FASLODEX® (Fulvestrant) is a selective estrogen receptor down-regulator presently indicated for the treatment of hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer patients, with disease progression following antiestrogen therapy.
Approximately 80% of breast tumors express Estrogen Receptors and/or Progesterone Receptors and these patients are often treated with anti-estrogen therapy as first line treatment. Cyclin Dependent Kinases (CDK) play a very important role to facilitate orderly and controlled progression of the cell cycle. Genetic alterations in these kinases and their regulatory proteins have been implicated in various malignancies. Cyclin Dependent Kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4 and CDK6) phosphorylate RetinoBlastoma protein (RB) and initiate transition from the G1 phase to the S phase of the cell cycle. CDK4 and CDK6 are activated in hormone receptor positive breast cancer, promoting breast cancer cell proliferation. Further, there is evidence to suggest that endocrine resistant breast cancer cell lines depend on CDK4 for cell proliferation. IBRANCE® (Palbociclib) is a reversible, oral, selective, small molecule inhibitor of Cyclin Dependent Kinases, CDK4 and CDK6, and prevent RB1 phosphorylation. IBRANCE® is the first CDK inhibitor approved by the FDA. It exhibits synergy when combined with endocrine therapies. In an open-label, randomized, phase II study, which included treatment naïve postmenopausal women with ER-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer, IBRANCE® given along with Aromatase Inhibitor FEMARA® (Letrozole) significantly prolonged Progression Free Survival, Overall Response rate and median duration of response, compared to FEMARA® alone. Based on this data, the U. S. Food and Drug Administration on February 3, 2015 granted accelerated approval to IBRANCE® (Palbociclib), for use in combination with FEMARA® (Letrozole) in this patient population. FASLODEX® (Fulvestrant) is a selective estrogen receptor down-regulator presently indicated for the treatment of hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer patients, with disease progression following antiestrogen therapy. Immune checkpoints are cell surface inhibitory proteins/receptors that are expressed on activated T cells. They harness the immune system and prevent uncontrolled immune reactions. Survival of cancer cells in the human body may be to a significant extent, related to their ability to escape immune surveillance, by inhibiting T lymphocyte activation. The T cells of the immune system therefore play a very important role in modulating the immune system. Under normal circumstances, inhibition of an intense immune response and switching off the T cells of the immune system, is an evolutionary mechanism and is accomplished by Immune checkpoints or gate keepers. With the recognition of Immune checkpoint proteins and their role in suppressing antitumor immunity, antibodies are being developed that target the membrane bound inhibitory Immune checkpoint proteins/receptors such as CTLA-4 (Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4), also known as CD152, PD-1(Programmed cell Death-1), etc. By doing so, one would expect to unleash the T cells, resulting in T cell proliferation, activation and a therapeutic response. The first Immune checkpoint protein to be clinically targeted was CTLA-4. YERVOY® (Ipilimumab), an antibody that blocks Immune checkpoint protein/receptor CTLA- 4, has been shown to prolong overall survival in patients with previously treated, unresectable or metastatic melanoma. KEYTRUDA® (Pembrolizumab) is a fully humanized, Immunoglobulin G4, monoclonal antibody, that binds to the PD-1 receptor and blocks its interaction with ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2, thereby undoing PD-1 pathway-mediated inhibition of the immune response and unleashing the tumor-specific effector T cells. The FDA granted accelerated approval to KEYTRUDA® in September 2014, for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma and disease progression following YERVOY® and, if BRAF V600 mutation positive, a BRAF inhibitor. The activity of KEYTRUDA® as a single agent in advanced SCCHN patients, was previously published and was noted in PD-L1 positive tumors, regardless of the Human PapillomaVirus (HPV) status. The Overall Response Rate in this patient group was 20% and 29% of patients had stable disease. The authors in this study reported the efficacy of once every three week dose of KEYTRUDA®, in a larger expansion cohort of KEYNOTE 012 study. In this study, 132 patients with recurrent/metastatic SCCHN were enrolled, regardless of their PD-L1 expression or HPV status. These patients received a fixed dose of KEYTRUDA® 200 mg IV, every 3 weeks and patients were evaluated every 8 weeks with radiographic imaging. The mean age was 59 years and 57% of the patients had 2 or more lines of therapy for recurrent disease. Treatment was continued until disease progression. The primary end point was Overall Response Rate (ORR) and secondary endpoints included Progression Free Survival (PFS) and Overall Survival (OS). The Overall Response Rate was 25% and stable disease was noted in an additional 25% of the patients. This amounted to a disease control rate of 50%. Patients with HPV-positive disease had a response rate of 20.6% and patients with HPV-negative disease had a response rate of 27.2%, suggesting that KEYTRUDA® was active in both subgroups of patients. Serious toxicities were reported in fewer than 10% of patients and the most common adverse event was fatigue (15.2%). The authors concluded that KEYTRUDA® given every 3 weeks was well tolerated and demonstrated a meaningful response rate in a heavily pretreated population of patients, with recurrent/metastatic SCCHN. Evaluation of PD-L1 status for this patient group is ongoing. Antitumor activity and safety of pembrolizumab in patients (pts) with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN): Preliminary results from KEYNOTE-012 expansion cohort. Seiwert TY, Haddad RI, Gupta S, et al. J Clin Oncol 33, 2015 (suppl; abstr LBA6008)</s
Immune checkpoints are cell surface inhibitory proteins/receptors that are expressed on activated T cells. They harness the immune system and prevent uncontrolled immune reactions. Survival of cancer cells in the human body may be to a significant extent, related to their ability to escape immune surveillance, by inhibiting T lymphocyte activation. The T cells of the immune system therefore play a very important role in modulating the immune system. Under normal circumstances, inhibition of an intense immune response and switching off the T cells of the immune system, is an evolutionary mechanism and is accomplished by Immune checkpoints or gate keepers. With the recognition of Immune checkpoint proteins and their role in suppressing antitumor immunity, antibodies are being developed that target the membrane bound inhibitory Immune checkpoint proteins/receptors such as CTLA-4 (Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4), also known as CD152, PD-1(Programmed cell Death-1), etc. By doing so, one would expect to unleash the T cells, resulting in T cell proliferation, activation and a therapeutic response. The first Immune checkpoint protein to be clinically targeted was CTLA-4. YERVOY® (Ipilimumab), an antibody that blocks Immune checkpoint protein/receptor CTLA- 4, has been shown to prolong overall survival in patients with previously treated, unresectable or metastatic melanoma. KEYTRUDA® (Pembrolizumab) is a fully humanized, Immunoglobulin G4, monoclonal antibody, that binds to the PD-1 receptor and blocks its interaction with ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2, thereby undoing PD-1 pathway-mediated inhibition of the immune response and unleashing the tumor-specific effector T cells. The FDA granted accelerated approval to KEYTRUDA® in September 2014, for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma and disease progression following YERVOY® and, if BRAF V600 mutation positive, a BRAF inhibitor. The activity of KEYTRUDA® as a single agent in advanced SCCHN patients, was previously published and was noted in PD-L1 positive tumors, regardless of the Human PapillomaVirus (HPV) status. The Overall Response Rate in this patient group was 20% and 29% of patients had stable disease. The authors in this study reported the efficacy of once every three week dose of KEYTRUDA®, in a larger expansion cohort of KEYNOTE 012 study. In this study, 132 patients with recurrent/metastatic SCCHN were enrolled, regardless of their PD-L1 expression or HPV status. These patients received a fixed dose of KEYTRUDA® 200 mg IV, every 3 weeks and patients were evaluated every 8 weeks with radiographic imaging. The mean age was 59 years and 57% of the patients had 2 or more lines of therapy for recurrent disease. Treatment was continued until disease progression. The primary end point was Overall Response Rate (ORR) and secondary endpoints included Progression Free Survival (PFS) and Overall Survival (OS). The Overall Response Rate was 25% and stable disease was noted in an additional 25% of the patients. This amounted to a disease control rate of 50%. Patients with HPV-positive disease had a response rate of 20.6% and patients with HPV-negative disease had a response rate of 27.2%, suggesting that KEYTRUDA® was active in both subgroups of patients. Serious toxicities were reported in fewer than 10% of patients and the most common adverse event was fatigue (15.2%). The authors concluded that KEYTRUDA® given every 3 weeks was well tolerated and demonstrated a meaningful response rate in a heavily pretreated population of patients, with recurrent/metastatic SCCHN. Evaluation of PD-L1 status for this patient group is ongoing. Antitumor activity and safety of pembrolizumab in patients (pts) with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN): Preliminary results from KEYNOTE-012 expansion cohort. Seiwert TY, Haddad RI, Gupta S, et al. J Clin Oncol 33, 2015 (suppl; abstr LBA6008)</s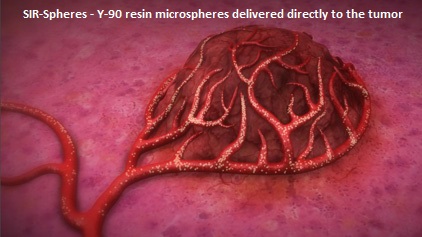 SIRFLOX is an International, multi-center, open-label, randomized phase III study, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of combining modified FOLFOX6 (Oxaliplatin, 5-FU and Leucovorin) chemotherapy regimen with or without AVASTIN® (Bevacizumab) with SIRT, using Y-90 resin microspheres, as first line treatment in patients with unresectable liver only or liver dominant metastatic ColoRectal Cancer (mCRC). The randomization included 530 patients of whom 263 patients received mFOLFOX6 with or without AVASTIN® (Group A) and 267 patients received mFOLFOX6 + SIRT administered once with cycle 1, with or without AVASTIN® (Group B), with the treatment given until disease progression. Patients were stratified based on the extent of liver involvement (25% or less versus more than 25%), presence of extra hepatic disease (liver only versus liver dominant disease) and treatment with AVASTIN®, which was at the discretion of the attending physician. Forty percent of the patients had extra hepatic disease. The primary endpoint was Progression Free Survival (PFS). With a median follow up of 36.1 months, the median PFS in the liver was 12.6 months versus 20.5 months in Group A versus Group B respectively (HR=0.69; P=0.002). The hepatic Response Rate was 68.8% versus 78.7% (P=0.042), with a Complete Response Rate of 1.9% versus 6.0% (P=0.02) in Groups A and B respectively. Even though hematologic and gastrointestinal adverse events were higher in the SIRT group, the toxicity levels were acceptable. The authors concluded that the addition of SIRT to chemotherapy resulted in a 7.9 month improvement in Progression Free Survival in the liver, for patients with unresectable metastatic ColoRectal cancer (mCRC), with a 31% reduction in the risk of tumor progression in the liver. With the liver being the most common site of spread in patients with metastatic CRC, this study provides Level One evidence to support the use of SIRT in combination with chemotherapy in this patient group. SIRFLOX: Randomized phase III trial comparing first-line mFOLFOX6 ± bevacizumab (bev) versus mFOLFOX6 + selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) ± bev in patients (pts) with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Gibbs P, Heinemann V, Sharma NK, et al. J Clin Oncol 33, 2015 (suppl; abstr 3502)</s
SIRFLOX is an International, multi-center, open-label, randomized phase III study, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of combining modified FOLFOX6 (Oxaliplatin, 5-FU and Leucovorin) chemotherapy regimen with or without AVASTIN® (Bevacizumab) with SIRT, using Y-90 resin microspheres, as first line treatment in patients with unresectable liver only or liver dominant metastatic ColoRectal Cancer (mCRC). The randomization included 530 patients of whom 263 patients received mFOLFOX6 with or without AVASTIN® (Group A) and 267 patients received mFOLFOX6 + SIRT administered once with cycle 1, with or without AVASTIN® (Group B), with the treatment given until disease progression. Patients were stratified based on the extent of liver involvement (25% or less versus more than 25%), presence of extra hepatic disease (liver only versus liver dominant disease) and treatment with AVASTIN®, which was at the discretion of the attending physician. Forty percent of the patients had extra hepatic disease. The primary endpoint was Progression Free Survival (PFS). With a median follow up of 36.1 months, the median PFS in the liver was 12.6 months versus 20.5 months in Group A versus Group B respectively (HR=0.69; P=0.002). The hepatic Response Rate was 68.8% versus 78.7% (P=0.042), with a Complete Response Rate of 1.9% versus 6.0% (P=0.02) in Groups A and B respectively. Even though hematologic and gastrointestinal adverse events were higher in the SIRT group, the toxicity levels were acceptable. The authors concluded that the addition of SIRT to chemotherapy resulted in a 7.9 month improvement in Progression Free Survival in the liver, for patients with unresectable metastatic ColoRectal cancer (mCRC), with a 31% reduction in the risk of tumor progression in the liver. With the liver being the most common site of spread in patients with metastatic CRC, this study provides Level One evidence to support the use of SIRT in combination with chemotherapy in this patient group. SIRFLOX: Randomized phase III trial comparing first-line mFOLFOX6 ± bevacizumab (bev) versus mFOLFOX6 + selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) ± bev in patients (pts) with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Gibbs P, Heinemann V, Sharma NK, et al. J Clin Oncol 33, 2015 (suppl; abstr 3502)</s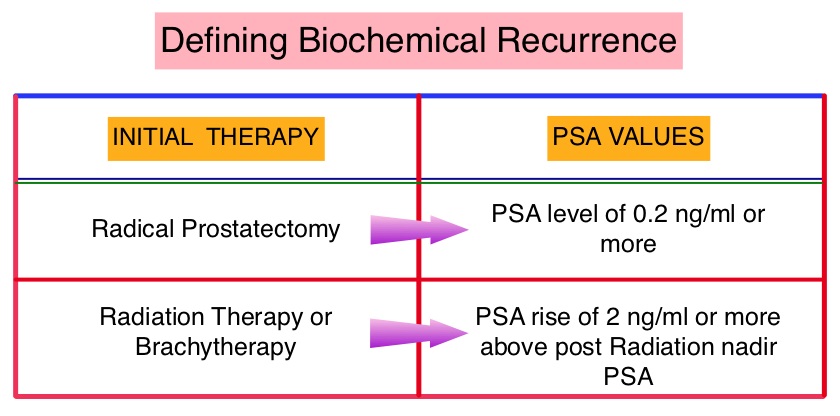 The American Urological Association suggested that a PSA of 0.2 ng/mL or higher after Radical Prostatectomy, defines PSA failure or relapse. A PSA rise of 2 ng/ml or more above post Radiation Therapy nadir is considered PSA failure or relapse. Approximately 35% of the patients with prostate cancer will experience PSA only relapse within 10 years of their primary treatment and a third of these patients will develop documented metastatic disease within 8 years following PSA only relapse. The development and progression of prostate cancer is driven by androgens. Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) has therefore been the cornerstone of treatment of advanced prostate cancer and is the first treatment intervention for hormone sensitive prostate cancer. The appropriate time (immediate versus delayed) to start Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) in patients with prostate cancer with rising Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA), as the only sign of relapse, has remained unclear. This has been partly due to lack of patient accruals and patient reluctance to be randomized, in these clinical trials.
The American Urological Association suggested that a PSA of 0.2 ng/mL or higher after Radical Prostatectomy, defines PSA failure or relapse. A PSA rise of 2 ng/ml or more above post Radiation Therapy nadir is considered PSA failure or relapse. Approximately 35% of the patients with prostate cancer will experience PSA only relapse within 10 years of their primary treatment and a third of these patients will develop documented metastatic disease within 8 years following PSA only relapse. The development and progression of prostate cancer is driven by androgens. Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) has therefore been the cornerstone of treatment of advanced prostate cancer and is the first treatment intervention for hormone sensitive prostate cancer. The appropriate time (immediate versus delayed) to start Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) in patients with prostate cancer with rising Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA), as the only sign of relapse, has remained unclear. This has been partly due to lack of patient accruals and patient reluctance to be randomized, in these clinical trials.
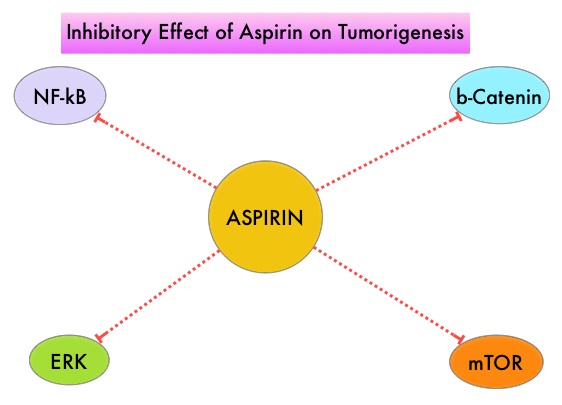 It is postulated that Aspirin also works by COX-independent mechanisms such as, the inhibition of NF-kB and Wnt/ β-catenin signaling, which may play a role in its chemopreventive properties. Even though the benefits of Aspirin in the primary prevention of CRC remains well established, the role of Aspirin in secondary prevention in patients with CRC is unclear. The authors conducted this trial to evaluate the association between Aspirin use after diagnosis of CRC with CRC-Specific Survival (CSS) and Overall Survival (OS) in the largest group of patients ever studied. The study authors in this retrospective study identified 25,644 patients in the Cancer Registry of Norway, diagnosed with ColoRectal Cancer (CRC) from 2004 through 2011. Using the Norwegian Prescription Database, the authors were then able to establish that 6,109 patients in this large cohort had documented exposure to Aspirin. Exposure to Aspirin was defined as a prescription for more than 6 months of Aspirin following a diagnosis of CRC. The median follow up was 2.2 years. The authors performed a multivariate regression analysis controlling for age, gender, tumor stage, tumor differentiation and noted that exposure to Aspirin post-diagnosis, independently improved ColoRectal Cancer (CRC) -Specific Survival (HR=0.75; P<0.001) and Overall Survival (HR=0.86; P<0.001). The authors concluded that in this large group of unselected ColoRectal Cancer (CRC) patients, exposure to Aspirin after the diagnosis of CRC is independently associated with improved Colorectal Cancer-Specific Survival and Overall Survival. They added that because of the risk of bleeding, the risk–benefit should be assessed before Aspirin is routinely recommended to this patient population. Impact of aspirin as secondary prevention in an unselected cohort of 25,644 patients with colorectal cancer: A population-based study. Bains S, Mahic M, Cvancarova M, et al. J Clin Oncol 33, 2015 (suppl; abstr 3504)
It is postulated that Aspirin also works by COX-independent mechanisms such as, the inhibition of NF-kB and Wnt/ β-catenin signaling, which may play a role in its chemopreventive properties. Even though the benefits of Aspirin in the primary prevention of CRC remains well established, the role of Aspirin in secondary prevention in patients with CRC is unclear. The authors conducted this trial to evaluate the association between Aspirin use after diagnosis of CRC with CRC-Specific Survival (CSS) and Overall Survival (OS) in the largest group of patients ever studied. The study authors in this retrospective study identified 25,644 patients in the Cancer Registry of Norway, diagnosed with ColoRectal Cancer (CRC) from 2004 through 2011. Using the Norwegian Prescription Database, the authors were then able to establish that 6,109 patients in this large cohort had documented exposure to Aspirin. Exposure to Aspirin was defined as a prescription for more than 6 months of Aspirin following a diagnosis of CRC. The median follow up was 2.2 years. The authors performed a multivariate regression analysis controlling for age, gender, tumor stage, tumor differentiation and noted that exposure to Aspirin post-diagnosis, independently improved ColoRectal Cancer (CRC) -Specific Survival (HR=0.75; P<0.001) and Overall Survival (HR=0.86; P<0.001). The authors concluded that in this large group of unselected ColoRectal Cancer (CRC) patients, exposure to Aspirin after the diagnosis of CRC is independently associated with improved Colorectal Cancer-Specific Survival and Overall Survival. They added that because of the risk of bleeding, the risk–benefit should be assessed before Aspirin is routinely recommended to this patient population. Impact of aspirin as secondary prevention in an unselected cohort of 25,644 patients with colorectal cancer: A population-based study. Bains S, Mahic M, Cvancarova M, et al. J Clin Oncol 33, 2015 (suppl; abstr 3504)