The FDA granted ZYDELIG®, accelerated approval in relapsed Follicular B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma and Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma. The approval was based on ZYDELIG®’s significant single agent activity with an acceptable safety profile, in heavily pretreated patients with indolent Non Hodgkin Lymphomas. ZYDELIG® is a highly selective, small molecule, oral inhibitor of the enzyme Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase delta (PI3K delta) and blocks the delta isoform of PI3K enzyme and its signaling pathway, thus promoting apoptosis. More information is available at www.oncoprescribe.com
Tag: Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
PI3Kδ Inhibition by Idelalisib in Patients with Relapsed Indolent Lymphoma
SUMMARY: Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) is one of the most common cancers in the United States and the American Cancer Society estimates that in 2014, about 70,800 people will be diagnosed with NHL in the US and close to 19,000 people will die of the disease. PI3K delta signaling is hyperactive in B-cell malignancies and is important for the activation, proliferation, homing of malignant B cells in the lymphoid tissues and their survival. PI3K (PhosphatidylInositol 3-Kinase) is a lipid kinase and has four distinct isoforms – alpha, beta, gamma and delta. The alpha and beta isoforms are expressed in a wide variety of tissues whereas the gamma and delta isoforms are only expressed in hematopoietic cells. PI3K delta (the delta isoform of PI3K enzyme) is predominantly expressed in leukocytes and plays an important role in the normal B lymphocyte development as well as signal transduction from B cell receptor as well as receptors for various cytokines and chemokines.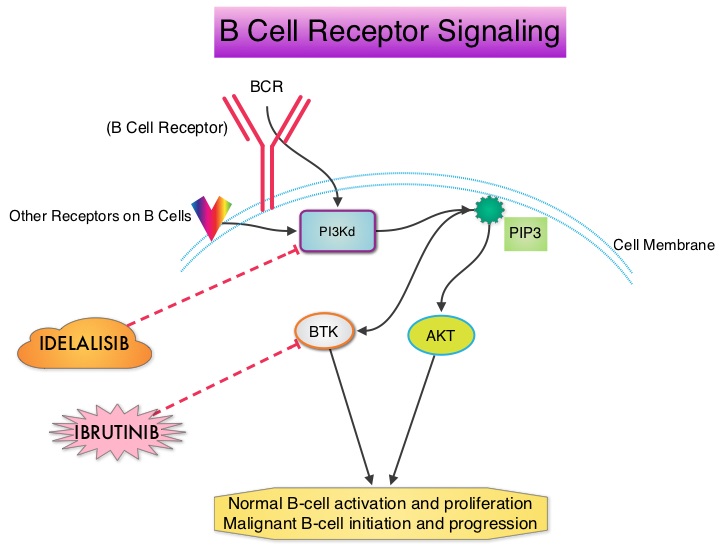 PI3K delta is activated by BCR signaling resulting in the production of a second messenger, Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) which in turn activates Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) and AKT, a prosurvival kinase. Idelalisib (ZYDELIG®) is a highly selective, small molecule, oral inhibitor of the enzyme Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase delta (PI3K delta) and blocks the delta isoform of PI3K enzyme and its signaling pathway, thus promoting apoptosis. The FDA granted ZYDELIG® accelerated approval in relapsed Follicular B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma and Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma based on the results of a single-arm, open-label, phase II trial. Patients with indolent Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas (N=125), who were refractory to Rituximab (RITUXAN®) and an alkylating agent or had relapsed within 6 months after receipt of these therapies, received ZYDELIG®, 150 mg PO BID. Treatment was continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicities developed. The median age was 64 years and enrolled patients had received a median of four prior therapies. The indolent Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma subtypes included Follicular lymphoma (N=72), Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (N=28), Marginal Zone Lymphoma (N=15), and Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma with or without Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia (N=10). The primary end point of this study was Overall Response Rate and secondary end points included the Duration of Response, Progression Free Survival, and Safety. The median follow up was 9.7 months. The Overall Response Rate was 57% with 50% partial responses and 6% complete responses. There was no difference in the Reponse Rates across the various subtypes of Indolent Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. The median time to response was 1.9 months and the median duration of response was 12.5 months. The median Progression Free Survival was 11 months and the Overall Survival at one year was estimated to be 80%. The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were diarrhea (13%), neutropenia (27%) and elevations in SGOT and SGPT levels (13%). These toxicities were manageable with dose modifications and dose interruptions. The authors concluded that ZYDELIG® has significant single agent activity, with an acceptable safety profile, in heavily pretreated patients with indolent Non Hodgkin Lymphomas. Gopal AK, Kahl BS, de Vos S, et al. N Engl J Med 2014; 370:1008-1018
PI3K delta is activated by BCR signaling resulting in the production of a second messenger, Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3) which in turn activates Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) and AKT, a prosurvival kinase. Idelalisib (ZYDELIG®) is a highly selective, small molecule, oral inhibitor of the enzyme Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase delta (PI3K delta) and blocks the delta isoform of PI3K enzyme and its signaling pathway, thus promoting apoptosis. The FDA granted ZYDELIG® accelerated approval in relapsed Follicular B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma and Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma based on the results of a single-arm, open-label, phase II trial. Patients with indolent Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas (N=125), who were refractory to Rituximab (RITUXAN®) and an alkylating agent or had relapsed within 6 months after receipt of these therapies, received ZYDELIG®, 150 mg PO BID. Treatment was continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicities developed. The median age was 64 years and enrolled patients had received a median of four prior therapies. The indolent Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma subtypes included Follicular lymphoma (N=72), Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (N=28), Marginal Zone Lymphoma (N=15), and Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma with or without Waldenström's Macroglobulinemia (N=10). The primary end point of this study was Overall Response Rate and secondary end points included the Duration of Response, Progression Free Survival, and Safety. The median follow up was 9.7 months. The Overall Response Rate was 57% with 50% partial responses and 6% complete responses. There was no difference in the Reponse Rates across the various subtypes of Indolent Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. The median time to response was 1.9 months and the median duration of response was 12.5 months. The median Progression Free Survival was 11 months and the Overall Survival at one year was estimated to be 80%. The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were diarrhea (13%), neutropenia (27%) and elevations in SGOT and SGPT levels (13%). These toxicities were manageable with dose modifications and dose interruptions. The authors concluded that ZYDELIG® has significant single agent activity, with an acceptable safety profile, in heavily pretreated patients with indolent Non Hodgkin Lymphomas. Gopal AK, Kahl BS, de Vos S, et al. N Engl J Med 2014; 370:1008-1018
Belinostat, a novel pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi), in relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (R/R PTCL) Results from the BELIEF trial
SUMMARY: Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is one of the most common cancers in the United States and the American Cancer Society estimates that in 2014, about 70,800 people will be diagnosed with NHL in the US and close to 19,000 people will die of the disease. T cell Lymphomas are a heterogenous group of lymphoid malignancies representing less than 15% of all Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas.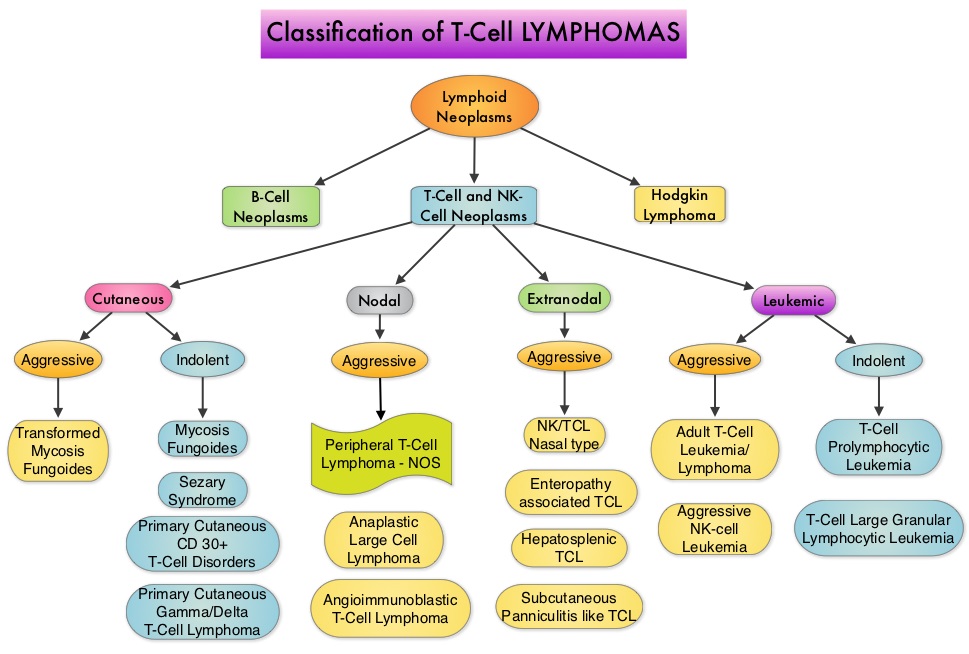
 Peripheral T-cell lymphoma – NOS (PTCL-Not Otherwise Specified) is the most common of the aggressive T-cell lymphoma subtypes and accounts for 26% of all non-cutaneous PTCL’s. These malignancies are derived from mature post thymic T-cells and NK cells. These tumors are uncommon, tend to be aggressive and majority of the patients with T-cell lymphoma present with advanced stage disease and respond poorly to treatment. Relapse rates tend to be high and few patients achieve durable remission with treatment. For these reasons, prognosis remains poor. Agents from two pharmacological classes are presently available for the treatment of PTCL. The FDA granted accelerated approval to FOLOTYN® (Pralatrexate), an antifolate, in 2009, for use in patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL and to ISTODAX® (Romidepsin), a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor in 2011, for the treatment of PTCL patients, who had received at least one prior therapy.
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma – NOS (PTCL-Not Otherwise Specified) is the most common of the aggressive T-cell lymphoma subtypes and accounts for 26% of all non-cutaneous PTCL’s. These malignancies are derived from mature post thymic T-cells and NK cells. These tumors are uncommon, tend to be aggressive and majority of the patients with T-cell lymphoma present with advanced stage disease and respond poorly to treatment. Relapse rates tend to be high and few patients achieve durable remission with treatment. For these reasons, prognosis remains poor. Agents from two pharmacological classes are presently available for the treatment of PTCL. The FDA granted accelerated approval to FOLOTYN® (Pralatrexate), an antifolate, in 2009, for use in patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL and to ISTODAX® (Romidepsin), a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor in 2011, for the treatment of PTCL patients, who had received at least one prior therapy.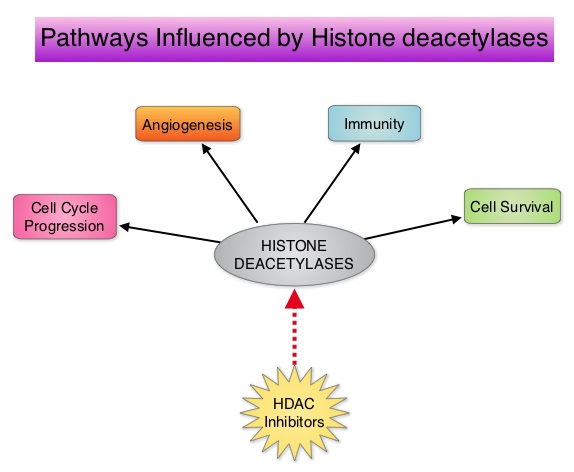 HDACs are a family of enzymes that play an important role in the regulation of gene expression. To briefly summarize the structure of a chromosome, individual loops of coiled double-helix DNA wrap around a histone protein to form a nucleosome. Nucleosomes are then coiled together to form chromatin fibers, which looks like beads on a string. The chromatin fibers are coiled even more tightly to form chromosomes. HDAC enzymes catalyze the removal of acetyl groups and regulate the level of acetylation of the histones and non-histone proteins and transcription of several genes. Hypoacetylation of histones has been associated with a condensed chromatin structure that results in the repression of gene transcription, whereas acetylated histones are associated with a more open chromatin structure and activation of gene transcription. HDACs are grouped into four major classes and regulate cell-cycle progression, cell survival, angiogenesis and immunity. BELEODAQ® (Belinostat) is a novel pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor and inhibits all 3 classes of the zinc-dependent HDAC enzymes.
HDACs are a family of enzymes that play an important role in the regulation of gene expression. To briefly summarize the structure of a chromosome, individual loops of coiled double-helix DNA wrap around a histone protein to form a nucleosome. Nucleosomes are then coiled together to form chromatin fibers, which looks like beads on a string. The chromatin fibers are coiled even more tightly to form chromosomes. HDAC enzymes catalyze the removal of acetyl groups and regulate the level of acetylation of the histones and non-histone proteins and transcription of several genes. Hypoacetylation of histones has been associated with a condensed chromatin structure that results in the repression of gene transcription, whereas acetylated histones are associated with a more open chromatin structure and activation of gene transcription. HDACs are grouped into four major classes and regulate cell-cycle progression, cell survival, angiogenesis and immunity. BELEODAQ® (Belinostat) is a novel pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor and inhibits all 3 classes of the zinc-dependent HDAC enzymes.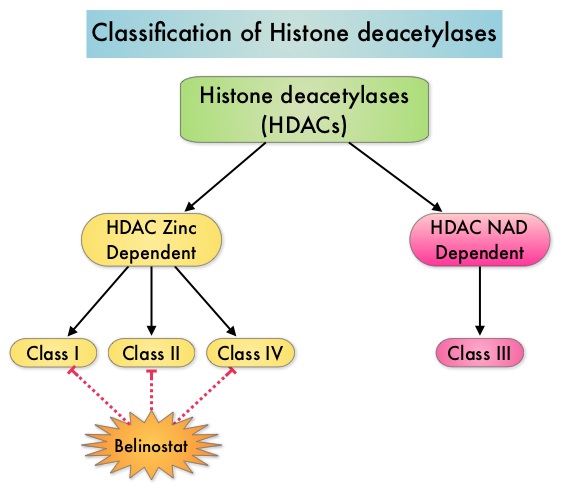 The approval of BELEODAQ® was based on the results of a multi-center, single-arm, phase II trial, in which 129 patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL, who had received a median of 2 prior therapies, were enrolled and evaluated. BELEODAQ® was administered as a 30 minute IV infusion at 1000 mg/m2 on days 1–5 of a 3 week cycle until progression or unacceptable toxicity. The median age was 63 years. The primary endpoint was Overall Response Rate (ORR). The ORR was 26% with 10% Complete Responses and 10% Partial responses and the median time to response was 5.6 weeks and the median duration of response was 8.3 months. The most common adverse events were nausea, vomiting, fatigue, fever and anemia. The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were thrombocytopenia (13%), neutropenia (13%), anemia (10%), dyspnea (6%), pneumonia (6%), and fatigue (5%). The authors concluded that BELEODAQ® demonstrated a significant overall response rate in relapsed /refractory PTCL patients, thus expanding the treatment options for these difficult to treat individuals. This was accomplished with a low incidence of myelosuppression and favorable safety profile. O'Connor OA, Masszi T, Savage KJ, et al. J Clin Oncol 31, 2013 (suppl; abstr 8507)
The approval of BELEODAQ® was based on the results of a multi-center, single-arm, phase II trial, in which 129 patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL, who had received a median of 2 prior therapies, were enrolled and evaluated. BELEODAQ® was administered as a 30 minute IV infusion at 1000 mg/m2 on days 1–5 of a 3 week cycle until progression or unacceptable toxicity. The median age was 63 years. The primary endpoint was Overall Response Rate (ORR). The ORR was 26% with 10% Complete Responses and 10% Partial responses and the median time to response was 5.6 weeks and the median duration of response was 8.3 months. The most common adverse events were nausea, vomiting, fatigue, fever and anemia. The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were thrombocytopenia (13%), neutropenia (13%), anemia (10%), dyspnea (6%), pneumonia (6%), and fatigue (5%). The authors concluded that BELEODAQ® demonstrated a significant overall response rate in relapsed /refractory PTCL patients, thus expanding the treatment options for these difficult to treat individuals. This was accomplished with a low incidence of myelosuppression and favorable safety profile. O'Connor OA, Masszi T, Savage KJ, et al. J Clin Oncol 31, 2013 (suppl; abstr 8507)
ZYDELIG® (Idelalisib)
The FDA on July 23, 2014 granted accelerated approval to ZYDELIG® for the treatment of patients with relapsed Follicular B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (FL) or relapsed Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL) who have received at least two prior systemic therapies. ZYDELIG® tablets are a product of Gilead Sciences, Inc.
BELEODAQ® (Belinostat)
The FDA on July 3, 2014 granted accelerated approval to BELEODAQ® for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma (PTCL). BELEODAQ® is a product of Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study Of The Efficacy and Safety Of Siltuximab, An Anti-Interleukin-6 Monoclonal Antibody, In Patients With Multicentric Castleman’s Disease
SUMMARY: Castleman Disease (CD) also known as giant lymph node hyperplasia and angiofollicular lymph node hyperplasia is a disease of lymph nodes and related tissues and can be Unicentric (localized) or Multicentric. Younger individuals are more likely to have the localized form whereas older adults and those with HIV infection are more likely to have the Multicentric form. Unicentric CD only affects a single group of lymph nodes and curative resection of the affected lymph nodes is feasible. Multicentric Castleman Disease (MCD) behaves like a lymphoma and is classified as a lymphoproliferative disorder and requires treatment intervention. The number of people diagnosed with MCD has been increasing with the rising incidence of HIV infection. Even though retroviral therapies have improved survival in patients with HIV infection, this has not impacted the incidence of MCD. Approximately 50% of the MCD cases have been attributed to Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated Herpes Virus (KSHV), also known as HHV-8, a gamma herpes virus which is a causative factor for Kaposi's sarcoma and Primary Effusion Lymphoma, while the cause of the remainder of the MCD cases is unknown. There are three microscopic subtypes of CD – The hyaline vascular type which is localized (Unicentric) type, the plasma cell type which is more likely to be Multicentric, and the mixed subtype which occurs less often. The microscopic findings are less important when it comes to treatment whereas treatment is based on whether the disease is Unicentric or Multicentric. KSHV is closely associated with plasmacytic form of MCD while the hyaline vascular type is generally negative for KSHV. Patients with Multicentric CD usually experience fevers, night sweats, weight loss, fatigue as well as leukocytopenia, hypergammaglobulinemia, generalized lymphadenopathy and possible splenic involvement. It resembles angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy and the symptoms and signs have been attributed to dysregulated interleukin (IL)-6 production. Some patients with CD may have normal IL-6 levels and present with microcytic anemia without iron deficiency, which resolves after effective therapy. MCD is seen in patients with POEMS syndrome (Polyneuropathy, Organomegaly, Endocrinopathy, M-protein, Skin changes) and has been implicated in 10% of cases of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Based on the preliminary data demonstrating the efficacy of SYLVANT® (Siltuximab), a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting human IL-6, in MCD patients, an international, multicenter, randomized phase II trial was conducted. Patients with Multicentric Castleman Disease (MCD) who were Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) negative and Human Herpes Virus-8 (HHV-8) negative (N=79) were randomized 2:1 to receive SYLVANT® (Siltuximab) given every three weeks, as an IV infusion at a dose of 11 mg/kg along with Best Supportive Care (N=53) or Placebo plus Best Supportive Care (N=26). The median age was 48 yrs, 30% were on corticosteroids and 58% had prior systemic therapy. Primary endpoint was durable tumor and symptomatic response defined as PR or CR by independent review and improvement or stabilization in MCD-related symptoms for 18 weeks or more. Secondary endpoints included additional predefined efficacy measures and safety. The durable tumor and symptomatic response rates (Primary endpoint) were 34% versus 0% for the SYLVANT® and Placebo groups respectively (P=0.0012). With regards to secondary endpoints, tumor response rates were 38% versus 4% for the SYLVANT® and placebo groups, respectively (P<0.05), the median time to treatment failure was 134 days in those receiving placebo and had not been reached in the SYLVANT® (P=0.0084), an increase in the hemoglobin of at least 1.5 grams/dL at week13 in anemic patients was seen in 61% of the patients receiving SYLVANT® vs 0% in those receiving Placebo (P=0.0002). There were sustained decreases in C-Reactive Protein (a marker of IL-6 activity), ESR, and fibrinogen as well as an increase in albumin in the SYLVANT® group. The common adverse reactions (>10% compared to placebo) during treatment with SYLVANT® were pruritus, weight gain, rash, hyperuricemia and upper respiratory tract infections. The authors concluded that this is the first randomized study involving patients with Multicentric Castleman Disease, that has demonstrated significant efficacy with SYLVANT®, resulting in durable tumor and symptom responses and added clinical benefit. Wong RS, Casper C, Munshi N, et al. Abstract #505. ASH Annual Meeting and Exposition, 2013
There are three microscopic subtypes of CD – The hyaline vascular type which is localized (Unicentric) type, the plasma cell type which is more likely to be Multicentric, and the mixed subtype which occurs less often. The microscopic findings are less important when it comes to treatment whereas treatment is based on whether the disease is Unicentric or Multicentric. KSHV is closely associated with plasmacytic form of MCD while the hyaline vascular type is generally negative for KSHV. Patients with Multicentric CD usually experience fevers, night sweats, weight loss, fatigue as well as leukocytopenia, hypergammaglobulinemia, generalized lymphadenopathy and possible splenic involvement. It resembles angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy and the symptoms and signs have been attributed to dysregulated interleukin (IL)-6 production. Some patients with CD may have normal IL-6 levels and present with microcytic anemia without iron deficiency, which resolves after effective therapy. MCD is seen in patients with POEMS syndrome (Polyneuropathy, Organomegaly, Endocrinopathy, M-protein, Skin changes) and has been implicated in 10% of cases of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Based on the preliminary data demonstrating the efficacy of SYLVANT® (Siltuximab), a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting human IL-6, in MCD patients, an international, multicenter, randomized phase II trial was conducted. Patients with Multicentric Castleman Disease (MCD) who were Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) negative and Human Herpes Virus-8 (HHV-8) negative (N=79) were randomized 2:1 to receive SYLVANT® (Siltuximab) given every three weeks, as an IV infusion at a dose of 11 mg/kg along with Best Supportive Care (N=53) or Placebo plus Best Supportive Care (N=26). The median age was 48 yrs, 30% were on corticosteroids and 58% had prior systemic therapy. Primary endpoint was durable tumor and symptomatic response defined as PR or CR by independent review and improvement or stabilization in MCD-related symptoms for 18 weeks or more. Secondary endpoints included additional predefined efficacy measures and safety. The durable tumor and symptomatic response rates (Primary endpoint) were 34% versus 0% for the SYLVANT® and Placebo groups respectively (P=0.0012). With regards to secondary endpoints, tumor response rates were 38% versus 4% for the SYLVANT® and placebo groups, respectively (P<0.05), the median time to treatment failure was 134 days in those receiving placebo and had not been reached in the SYLVANT® (P=0.0084), an increase in the hemoglobin of at least 1.5 grams/dL at week13 in anemic patients was seen in 61% of the patients receiving SYLVANT® vs 0% in those receiving Placebo (P=0.0002). There were sustained decreases in C-Reactive Protein (a marker of IL-6 activity), ESR, and fibrinogen as well as an increase in albumin in the SYLVANT® group. The common adverse reactions (>10% compared to placebo) during treatment with SYLVANT® were pruritus, weight gain, rash, hyperuricemia and upper respiratory tract infections. The authors concluded that this is the first randomized study involving patients with Multicentric Castleman Disease, that has demonstrated significant efficacy with SYLVANT®, resulting in durable tumor and symptom responses and added clinical benefit. Wong RS, Casper C, Munshi N, et al. Abstract #505. ASH Annual Meeting and Exposition, 2013
Rituximab Maintenance Therapy Until Progression After Rituximab and Chemotherapy Induction in Patients With Follicular Lymphoma
SUMMARY: In this intriguing analysis, the authors reported the outcomes, when patients with low grade Follicular Lymphoma received maintenance RITUXAN® (Rituximab) beyond 2 years. The randomized, PRIMA (Primary Rituximab and Maintenance) study established that 2 years of RITUXAN® maintenance therapy after a RITUXAN® plus chemotherapy regimen, as first-line treatment for follicular lymphoma, significantly improves Progression Free Survival (PFS). The decision to give 2 years of maintenance RITUXAN® in the PRIMA study was arbitrary. It is estimated however that over 30% of the patients receiving 2 yrs of maintenance RITUXAN®, relapse at 3 years and beyond. The authors in this single institution study analyzed clinical data on 25 consecutive, unselected, treatment naïve patients with biopsy-proven diagnosis of Follicular Lymphoma. All these patients had a high tumor burden, with at least one indication for initiation of systemic therapy, which included B symptoms, cytopenia(s), bulky disease, disease progression, or impending organ damage. These patients achieved a Partial Response (PR) or a Complete Response (CR), after systemic induction treatment and subsequently received Maintenance RITUXAN® indefinitely or until disease progression. The median follow up was 5 years. The PFS in this group was 100% and 5 year overall survival was 82%. Forty five percent (45%) of the patients who achieved PR improved to CR on Maintenance RITUXAN® treatment. This benefit was accomplished with minimal toxicity with no additional complications related to hypogammaglobinemia. The authors concluded that Maintenance RITUXAN® beyond the arbitrary 2 years, is safe and may result in prolonged PFS in responding patients following chemoimmunotherapy. This provocative data begs the question whether maintenance RITUXAN® should be continued until disease progression rather than stopping at the 2 year arbitrary time frame. Yared J, Kimball A, Baer MR, et al. Clinical Lymphoma Myeloma and Leukemia 2013;13:253-257
Targeting BTK with Ibrutinib in Relapsed or Refractory Mantle-Cell Lymphoma
SUMMARY:The FDA granted accelerated approval to Ibrutinib (IMBRUVICA®), for the treatment of patients with Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL), who had received at least one prior therapy. Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) is a cytoplasmic protein predominantly expressed in B-cells and is a mediator of B-cell receptor signaling in normal and transformed B-cells. BTK is necessary for the proliferation and survival of B-cell tumors. IMBRUVICA® is an oral, irreversible inhibitor of BTK and thereby inhibits cell proliferation and promotes programmed cell death (Apoptosis). The efficacy of IMBRUVICA® was evaluated in a multi-center, international, single-arm Phase II trial in which 111 patients with previously treated MCL, received IMBRUVICA®, at a daily oral dose of 560 mg. The median age was 68 years and patients had received a median of three prior therapies. Patients were stratified into those who had previously received at least 2 cycles of VELCADE® (Bortezomib) therapy and those who had received less than 2 cycles or had no prior therapy with VELCADE®. More than 80% of patients had intermediate-risk or high-risk disease. Treatment was given until disease progression or until unacceptable toxicities were noted. The primary end point was Overall Response Rate (ORR). Secondary end points included duration of response, Progression Free Survival (PFS), Overall Survival (OS), and safety. With a median follow-up of 15.3 months, the ORR was 68%, with a 21% Complete Response and 47% Partial Response rate. The estimated median duration of response was 17.5 months. Prior treatment with VELCADE® had no influence on the Response Rate (RR). The median PFS was 13.9 months and estimated OS was 58% at 18 months. Treatment related toxicities were mild to moderate nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, and cytopenias. Grade 3 bleeding was noted in 5% of the patients, but these patients had a history of falls and were receiving either Aspirin or Warfarin. The authors concluded that IMBRUVICA® given as a single agent has durable efficacy in relapsed or refractory MCL. Studies are underway, combining IMBRUVICA® with TREANDA® (Bendamustine) and RITUXAN® (Rituximab), as front line therapy for patients with MCL. The list of agents for the treatment of relapsed or refractory MCL now include VELCADE®, REVLIMID® and IMBRUVICA®. Wang ML, Rule S, Martin P, et al. N Engl J Med 2013; 369:507-516
IMBRUVICA ® (Ibrutinib)
The FDA on November 13, 2013 granted accelerated approval to IMBRUVICA ® for the treatment of patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy. IMBRUVICA ® is an oral capsule and is a product of Pharmacyclics, Inc.
Single-Agent Lenalidomide in Patients With Mantle-Cell Lymphoma Who Relapsed or Progressed After or Were Refractory to Bortezomib Phase II MCL-001 (EMERGE) Study
SUMMARY: In the MCL-001 trial, 134 patients with relapsed or refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL) were enrolled. These patients had received prior treatment with RITUXAN® (Rituximab), CYTOXAN® (Cyclophosphamide), an Anthracycline and VELCADE® (Bortezomib) alone or in combination. The median age was 67 years and patients received a median of 4 prior therapies for MCL. Treatment consisted of Lenalidomide (REVLIMID®) 25 mg given orally on days 1 thru 21, of a 28 day cycle. Treatment was continued until disease progression or treatment intolerance. The primary efficacy endpoints were overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR). The secondary endpoints included Complete Response (CR), Progression Free Survival (PFS) and Overall Survival (OS). The ORR was 28% with a CR of 7% and the median DOR for those who responded to REVLIMID® was 16.6 months. The median PFS was 4 months and the median OS was 19 months.The most common grade 3-4 adverse reactions were cytopenias, fatigue, dyspnea and diarrhea. The authors concluded that REVLIMID® is the first drug to receive approval for the treatment of MCL since VELCADE® was approved for this disease in 2006 and gives one additional option for MCL patients, refractory to VELCADE®. Goy A, Sinha R, Williams ME, Besisik SK et al. J Clin Oncol 2013;31:3688-3695
